Why You Should Teach the Geography of Ancient Civilizations First
When diving into a new ancient civilization, it can be tempting to jump straight to kings, inventions, and famous battles. I’ve found that starting with the geography of ancient civilizations sets the stage for everything else our students will learn. If our kids don’t first understand where civilization existed in the world and what the land and climate were like, it’s harder for them to connect the dots when they get to culture, trade, politics, and daily life.
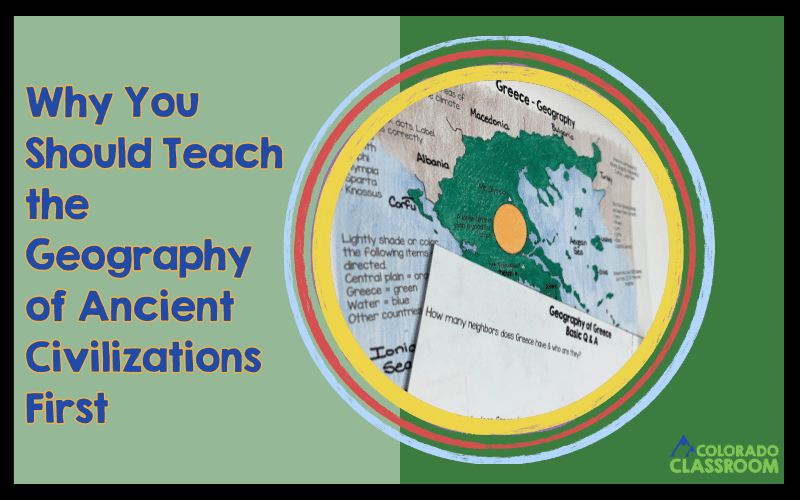
That’s why I love beginning each unit with a geography study. It’s not just about labeling rivers and mountains. It’s about giving our students a mental map they can carry with them through the rest of the unit. Once they can picture the terrain, climate, natural resources, and neighbors, they can better grasp why these civilizations developed the way they did.
The Geography of Ancient Civilizations as the Foundation for Learning

Geography shapes history. Whether it’s the fertile crescent of Mesopotamia, the mountainous terrain of Greece, or the Nile’s life-giving floodplains in Egypt, the geography of ancient civilizations determined where people could farm, how they traveled, and even how they interacted with neighboring cultures. By starting with this foundation, your students see history not as a random series of events, but as the result of real people adapting to their surroundings.
Why Geography Builds Better Scholars, Travelers, and Citizens
Teaching the geography of ancient civilizations is more than a history strategy. It’s character building. When your students understand how geography has shaped human decisions for thousands of years, they begin to think critically about the connections between environment and culture. This mindset makes them better scholars because they start looking for patterns, asking deeper questions, and using evidence to support their ideas.

It also makes them more adaptable travelers. A student who learns why ancient Greeks settled near the sea or why Egyptians built along the Nile is more likely to appreciate the natural and cultural features of places they visit in the future. They’ll notice the relationship between land and lifestyle wherever they go.
This kind of study fosters conscientious and culturally responsible citizens. Understanding that geography affects trade, migration, and cultural exchange helps your students respect and value differences in ways of life. It builds empathy, showing them that people throughout history and today have adapted to challenges and opportunities based on where they live.
Why Geography Still Matters
Studying the geography of ancient civilizations isn’t just about looking back. It’s about building skills and understanding that they are just as relevant today. The same mountains, rivers, deserts, and coastlines that influenced life thousands of years ago continue to shape how people live, work, and connect in our modern world.

When your students see that the Nile still supports agriculture in Egypt or that Greece’s harbors remain vital for trade, they realize geography is not just a history topic. It’s a living, breathing influence on economies, politics, and culture. Many modern cities sit where ancient ones once stood for the same reasons, such as access to water, fertile land, and trade routes. These connections help your students understand that geography isn’t frozen in time but evolves along with human needs.
By making these links, you’re giving your students tools to understand current events through a geographic lens. They start recognizing patterns. They’ll be able to see why certain areas are prone to conflict, why some regions lead in certain industries, and how climate and resources still play a role in shaping societies. The geography of ancient civilizations isn’t just the starting point of history. It’s a lens for understanding the world they live in right now.
Activities That Make the Geography of Ancient Civilizations Come Alive
One of the biggest advantages of teaching the geography of ancient civilizations first is that it’s highly interactive. My geography lessons for each civilization are packed with a variety of activities so your students stay engaged while building that essential background knowledge.
Each of my six geography lessons for ancient civilizations follows the same setup, so your students have a consistent learning experience. Every resource includes a blank map for labeling, an answer key map with a grading checklist, guided notes (in cloze or two-column format) with an answer key, a study guide, and a test. Your students explore both ancient and modern names, locate important cities, identify natural features, and connect these to farming, trade, and culture. This structure keeps things organized for you, as the teacher, and gives your students a predictable way to approach new content.
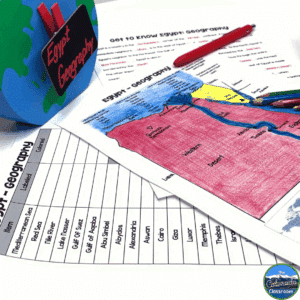
For example, the geography of ancient Egypt unit includes note-taking pages, close readings, and detailed map work where your students label seas, deserts, and the Nile River. In the geography of ancient Greece lesson, your students have the chance to explore how mountains led to the development of independent city-states and maritime trade. The Mesopotamia unit highlights the region’s unpredictable flooding and how it influenced farming and settlement patterns. China’s geography lesson dives into rivers like the Huang He and physical barriers like the Gobi Desert. India’s geography study focuses on the monsoons and their importance to agriculture. Italy’s geography work connects Rome’s position in the Mediterranean to its trade and expansion.
Across all six lessons, your students learn and identify ancient and modern names for locations, examine artifacts, and prepare for a study guide and test. This routine gives them consistent structure but keeps content fresh. They leave the geography portion of each unit ready to make meaningful connections when we shift into culture, government, and achievements.
When you start your units with the geography of ancient civilizations, you’re not just teaching maps. You’re giving your students the tools to think like historians. You’re helping them see the “why” behind the “what” of history. My geography lessons on Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, India, and Italy set the tone right from the start with notes, readings, maps, artifact studies, and assessments.
Ready to Go Beyond the Geography of Ancient Civilizations?

Starting with the geography of ancient civilizations is just the first step in creating a rich and engaging history unit. Once your students have that strong foundation, you can guide them through culture, government, daily life, achievements, and so much more.
I’ve put together complete units for Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, India, and Italy that build on these geography lessons. They give your students a well-rounded look at each civilization. Each unit includes interactive activities, structured notes, readings, maps, and assessments that work together for a complete learning experience. You can explore all of these resources in my store and start building your full ancient civilizations curriculum!
Save for Later
If you’re not quite ready to dive into teaching the geography of ancient civilizations, make sure to save this post so you can come back when you are. Pin it, bookmark it, or share it with a fellow teacher. You’ll be glad you have it on hand when it’s time to start your next unit.


